Transforming the lives of patients with severe insulin resistance
INSPARIN stands at the forefront of a new era in glucose management, offering innovative insulin-independent treatment options for patients with severe insulin resistance syndromes, rare genetic insulin receptor deficiencies, lipodystrophies and other metabolic diseases that affect mostly children and adolescents.
Our Science
Insulin-independent
pathways for Glucose Control
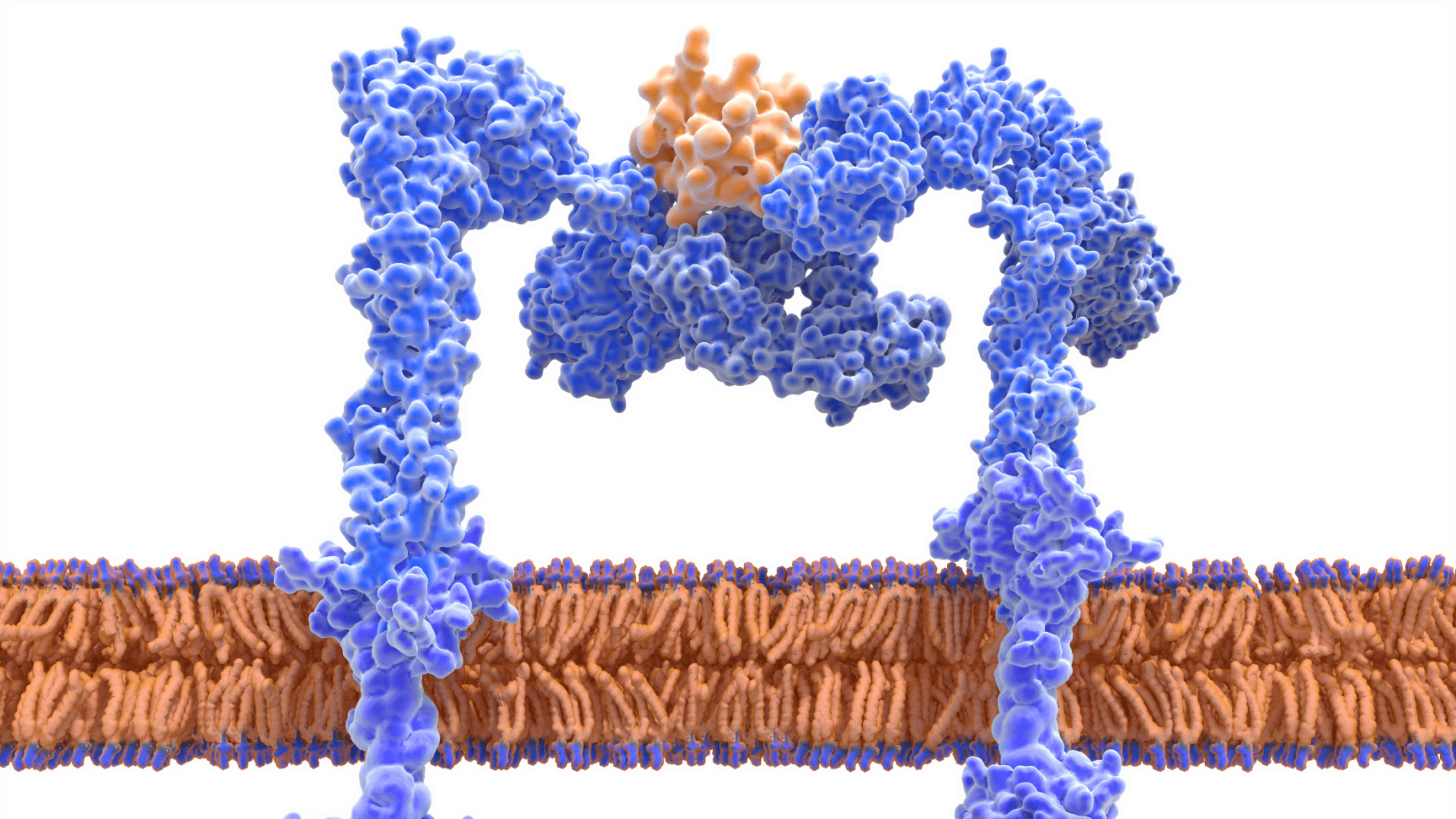
After years of groundbreaking research in understanding the adenovirus viral proteome, we discovered E4orf1, a protein with a unique mechanism to enhance glucose uptake and insulin utilization acting directly in muscle, liver and adipose tissue.
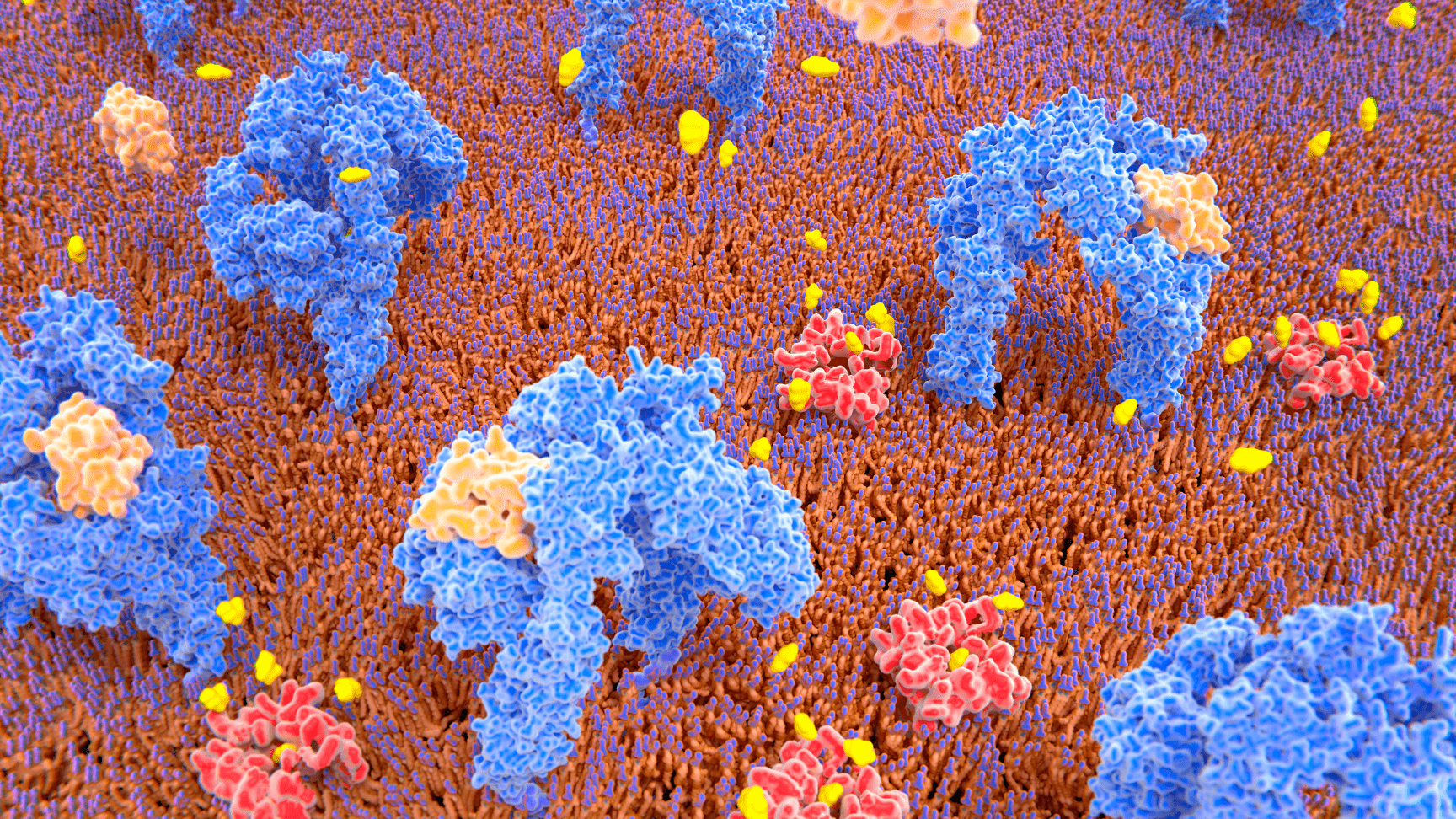
Unlike traditional diabetes therapies that require insulin to exert their effects, INSPARIN offers a discovery platform of first-in class pipeline therapeutic candidates to act via an insulin-independent pathway to control glucose uptake and optimize insulin requirements.
INSPARIN candidates become a promising choice for patients with severe defects in the insulin pathway and for those who are unable to produce sufficient amounts of insulin.
OUR PIPELINE
First-In-Class Candidates
Our therapeutic candidates are first-in-class of “insulin-sparing” compounds: treatments that act directly on muscle, liver and adipose cells to improve glycemic control independent of insulin.

Severe Insulin Resistance Syndromes
Severe insulin resistance syndromes, affect 0.1%–0.5% of children and young adults in diabetes clinics. This group of conditions are orphan rare diseases ranging from genetic insulin receptor abnormalities to lipodystrophies and other complex metabolic disorders that cause hyperinsulinemia and impaired glucose control. INSPARIN therapies target insulin-independent pathways, offering a groundbreaking alternative for improving blood glucose control and the quality of life for these underserved patients.
Severe Insulin Resistance in Type-1 and Type-2 Diabetes
INSPARIN holds the potential to significantly improve diabetes control and beta-cell health in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Up to 10% of people living with diabetes develop insulin resistance, commonly becoming a therapeutic and a clinical challenge. By enhancing glucose regulation without relying on insulin, INSPARIN could reduce the burden of frequent insulin injections, risk of hypoglycemia and overall offer a higher quality of life for patients.

Metabolic Syndrome
Beyond glucose control, INSPARIN shows promise in managing fatty liver conditions and metabolic syndrome, potentially reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. This further extends INSPARIN therapeutic reach, positioning it as a versatile treatment option for multiple metabolic and cardiovascular conditions.
get to know us
Our Team

Rohan DHURANDHAR
Chief Executive Officer

NIKHIL DHURANDHAR, Ph.d.
Founder and Chief Scientific Officer

VIJAY HEGDE, Ph.D.
Chief Research Officer

alexander gaidamaka, p.h.d., d.v.m.
Chief Technology Officer
cAREERS
Join Our Mission
Impact
Develop life-changing therapies that address severe insulin resistance and help patients who have no other options.
Innovation
Work at the forefront of scientific discovery, leveraging cutting-edge research to create first-in-class therapeutics.
Growth
Join a fast-moving startup where your contributions shape the company’s success and accelerate your career in biotech.
Ownership
Take full ownership of impactful projects from day one.
Interested? Email us at careers@insparin.com
NEWS
Press and Publications
Media Coverage
- Insparin Therapeutics Appoints Dr. Alex Gaidamaka as Chief Technology Officer
- Shining a Light on a Hidden Metabolic Crisis by Addressing the Unmet Need of Severe Insulin Resistance Syndromes
- Nutritional Sciences Faculty Awarded Grant for Innovative Insparin Drug Technology Research
- The Discovery of Insparin: A Game Changer for Diabetes and Steatosis
- Texas Tech Spinout On the Move; Insparin Therapeutics Secures Angel Funding, Presents A Novel Class of Diabetes Agent
- Texas Tech Spinoff Insparin Therapeutics: Developing Next Generation, Virus-based Diabetes & Obesity Therapies
Selected Publications
- Wang ZQ, Cefalu WT, Zhang XH, Yu Y, Qin J, Son L, Rogers PM, Mashtalir N, Bordelon J, Ye J and Dhurandhar NV. Human adenovirus type 36 enhances glucose uptake in diabetic and non-diabetic human skeletal muscle cells independent of insulin signaling. Diabetes. 2008; 57(7):1805-13.
- Peddibhotla S, Hegde V, Akheruzzaman M, Dhurandhar NV. E4orf1 protein reduces the need for endogenous insulin. Nutr Diabetes. 2019 May 24;9(1):17. doi: 10.1038/s41387-019-0085-x.
- Shastri AA, Hegde V, Peddibhotla S, Feizy Z, Dhurandhar NV. E4orf1: A Protein for Enhancing Glucose Uptake Despite Impaired Proximal Insulin Signaling. PLoS ONE 2018; Dec 6;13(12):e0208427.
- Akheruzzaman Md, Hegde V, Siddik AB, Feizy Z, Shin A, and Dhurandhar NV. E4orf1-induced reduction in endogenous insulin level is independent of pancreas endocrine function. Int J Obesity 2022 Jan 12. doi: 10.1038/s41366-021-01062-3.
- Feizy Z, Peddibhotla S, Khan S, Hegde V, Wang S, Dhurandhar NV. Nanoparticle-mediated in vitro delivery of E4orf1 to preadipocytes is a clinically relevant delivery system to improve glucose uptake Int J Obes (Lond). 2020 Jul;44(7):1607-1616. doi: 10.1038/s41366-020-0526-6